HOME < ABOUT US < PTFE COATING
PTFE COATING
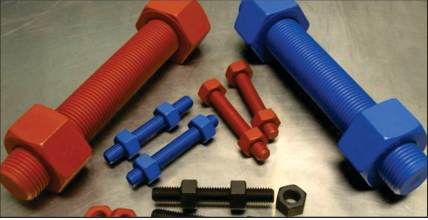

APPLICATIONS –
► The properties listed above show many of the properties that make PTFE a unique fluoropolymer. Because of these it has many advantages. The main ones are:
It is largely inert – this means it can be used to store reactive compounds or to line pipes that reactive agents will travel along
It is an excellent electrical insulator – this is why it is often used on printed circuit boards and electrical cables
► In addition, its abrasion-resistance is not as good as a number of other coatings and so abrasion resistance isn’t its primary advantage.
▸ Disadvantages of the material are only relative to the application: in many ways, PTFE is a wonder material but it can’t be used for everything. Depending on the application, the following disadvantages can rule out the selection of PTFE: ► Price – it is not a low-cost polymer
► Production sizes – it is not easy to mass produce
► It cannot be cemented
It can change shape under pressure
It cannot withstand extremely high temperatures and melts at 326 celsius
It can change shape under pressure
► It cannot withstand extremely high temperatures and melts at 326 celsius
BENEFITS
NON-STICK AND RELEASE- A PTFE coating applied to a component will give excellent non-stick/release properties and is very easy to clean. This type of coating is also excellent at preventing both hot and cold products from permanently sticking to the substrate and therefore is widely used in the cookware, confectionery, food processing and bakery industries. PTFE coatings are also used for non-stick in the packaging, heat sealing, moulding, automotive, aerospace, chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
NON-WETTING
PTFE surfaces are hydrophobic and oleophobic, and will not readily wet. This allows the material to self-clean. For the semiconductor industry, this property is vital as it allows all chemical media to run off and be collected.
STANCE
► PTFE coatings can service arduous application conditions involving extremes of temperature. They can remain stable
at advanced temperatures of +260°C and for short periods at +290°C. PTFE can be used on extrusion dies and sealing of plastic/elastomers where other treatments may degrade or cause clogging of molten material. These coatings can also perform at cryogenic temperatures and can remain stable at -270°C.
► LOW FRICTION AND ABRASION RESISTANCE
► PTFE coated surfaces reduce friction and can achieve very low coefficients of friction, typically from about 0.04 to 0.15. Where oils and grease evaporate at elevated temperatures PTFE remains and is therefore ideal for shafts, bearing surfaces, moving mechanisms, stud bolts and fasteners. For added abrasion resistance and increased wear life, this type of coating can be reinforced with the addition of fillers and also by combining with a metal sprayed base layer. CORROSION AND CHEMICAL RESISTANCE
► PTFE is inherently resistant to attack from most chemicals and when combined with other fluoropolymers such as FEP and PFA greatly enhances the life of the component. PTFE applied as a surface coating will increase the corrosion resistance of the component and can also be enhanced with the use of primers, other pre-treatments such as plating and phosphating. Stud bolts and fasteners, valves, pumps, pipe clamps and connectors all benefit from these types of coatings.
PTFE is inherently resistant to attack from most chemicals and when combined with other fluoropolymers such as FEP and PFA greatly enhances the life of the component. PTFE applied as a surface coating will increase the corrosion resistance of the component and can also be enhanced with the use of primers, other pre-treatments such as plating and phosphating. Stud bolts and fasteners, valves, pumps, pipe clamps and connectors all benefit from these types of coatings.
► PTFE coatings prevent galling and give excellent bearing properties. Mating surfaces and rotating parts benefit from this coating and help provide minimal maintenance downtime.


